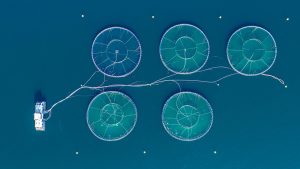
Offshore cages are large structures used in marine aquaculture, also known as fish farming. These cages are typically placed in the open ocean, often in sheltered bays or near coastlines. The purpose of these cages is to provide a controlled environment for the growth and cultivation of fish species, such as salmon, tilapia, and sea bass. They are typically made of metal or plastic materials and are anchored to the ocean floor to maintain stability and withstand the harsh conditions of the open ocean, such as strong currents, storms, and waves. The fish within the cages are fed and monitored, and the waste they produce is collected and disposed of properly to minimize environmental impact. Offshore cage systems are becoming increasingly popular as a way to meet the growing demand for seafood and provide a sustainable source of food for a growing global population.
There are several applications for offshore cages in aquaculture:
– Fish farming: Offshore cages are used to cultivate a variety of fish species for commercial purposes, such as salmon, tuna, and sea bass.
– Shellfish farming: The cages can also be used to grow shellfish, such as oysters, clams, and mussels.
– Research and development: Offshore cages can be used to test new species, breeding techniques, and farming methods in a controlled environment

1. Offshore aquaculture have several economic benefits, including:
– Increased food production: Offshore aquaculture provides a way to increase food production, meet the growing demand for seafood, and reduce the pressure on wild fish stocks.
– Economic growth: Offshore aquaculture can contribute to local and national economic growth by creating new industries and increasing exports.
– Reduced costs: Offshore aquaculture can reduce costs associated with traditional land-based farming methods, such as land acquisition and construction costs, as well as the cost of inputs such as feed and labor.
– Increased efficiency: Offshore aquaculture systems can be more efficient than traditional land-based methods, as they can be operated at a larger scale, with greater control over environmental conditions and feeding regimes.
It’s important to note that careful planning and management is essential to ensure that the economic benefits of offshore aquaculture are realized while minimizing any negative impacts.

2. Offshore aquaculture in cages also have several environmental benefits when compared to traditional land-based aquaculture methods. Some of these benefits include:
– Reduced pollution: Offshore aquaculture can help to reduce the environmental impact of land-based aquaculture. The waste produced by the fish and other species is dispersed into the surrounding ocean, reducing the risk of pollution in coastal areas.
– Habitat protection: By moving aquaculture operations offshore, the use of coastal habitats can be reduced, preserving these important ecosystems.
– Better water quality: Offshore aquaculture can help to improve the water quality of coastal areas by reducing the risk of pollution and maintaining the natural flow of water in the ocean.
– Increased sustainability: Offshore aquaculture can be more sustainable than land-based aquaculture because it utilizes the natural resources of the ocean, such as the sun and sea currents, to support growth and production.

3. Reduced disease risk: By placing the cages in open water, they are less susceptible to disease outbreaks and parasites compared to onshore or nearshore farms.
4. Space utilization: Offshore cages make efficient use of space as they can be located in areas with high ocean currents, which provide a continuous supply of fresh water and nutrients to the aquatic species.
1. High costs: The construction and maintenance of offshore cages are more expensive compared to onshore or nearshore farms.
2. Operational challenges: Offshore cages are subject to harsh weather conditions and can be challenging to operate and maintain due to their remote location and the need for specialized equipment and personnel.
3. Impacts on marine life: Offshore cages can have negative impacts on the surrounding marine environment and wildlife, including the introduction of non-native species and the accumulation of waste and chemicals.
4. Lack of control: Offshore cages can be vulnerable to theft, and environmental hazards, such as storms, strong currents, and contamination.
It is important for the industry to implement best practices and proper management techniques to minimize these impacts.